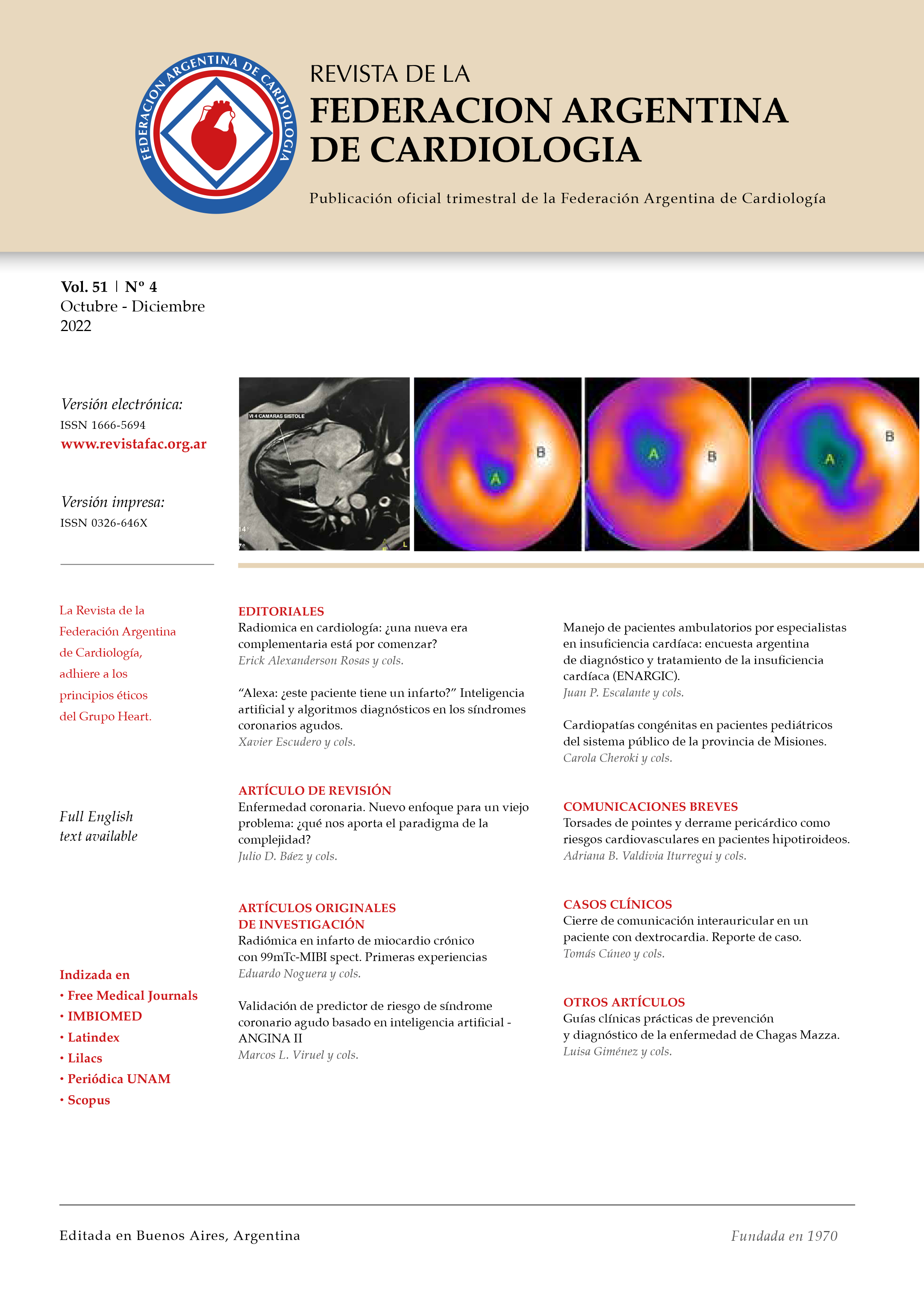
Radiomics in chronic myocardial infarction with 99MTC-MIBI SPEC. First experiences
Keywords:
Radiomics, Machine learning, Myocardial perfusion single photon emission computed tomography, Chronic myocardial infarctionAbstract
Objective: To investigate whether radiomics allows the detection of heterogeneity in fixed perfusion defects due to chronic myocardial infarction, in SPECT myocardial perfusion images with 99mTc-MIBI. Material and methods: Outpatient, single-center, retrospective cohort study. Twenty-eight patients (20 men and 8 women) (age 67 ± 11 years) with chronic myocardial infarction, with fixed perfusion defects in the image of the polar maps at rest, were consecutively included. Radiomica was extracted with the MaZda software, from regions of interest in the fixed defects with probable heterogeneous uptake and in the myocardium with homogeneous uptake, and subsequently analyzed with the RandomForest / LogitBoost algorithms included in the WEKA artificial intelligence program, which classified the textures heterogeneous vs. homogeneous with sensitivity, specificity and area under ROC curve (AUC) of 100%. Binomial logistic regression analysis showed that the heterogeneous textures 135dr_ShrtREmp, 45dgr_ShrtREmp, 45dgr_Fraction, S (2,-2) InvDfMom, Horzl_Fraction, which correspond to the co-occurrence matrix and run-length matrix, were significantly higher than the homogeneous with AUC of 100%. Conclusion: radiomics predicts and quantifies heterogeneity in fixed perfusion defects and provides potential future application to myocardial perfusion SPECT in patients with chronic myocardial infarction.