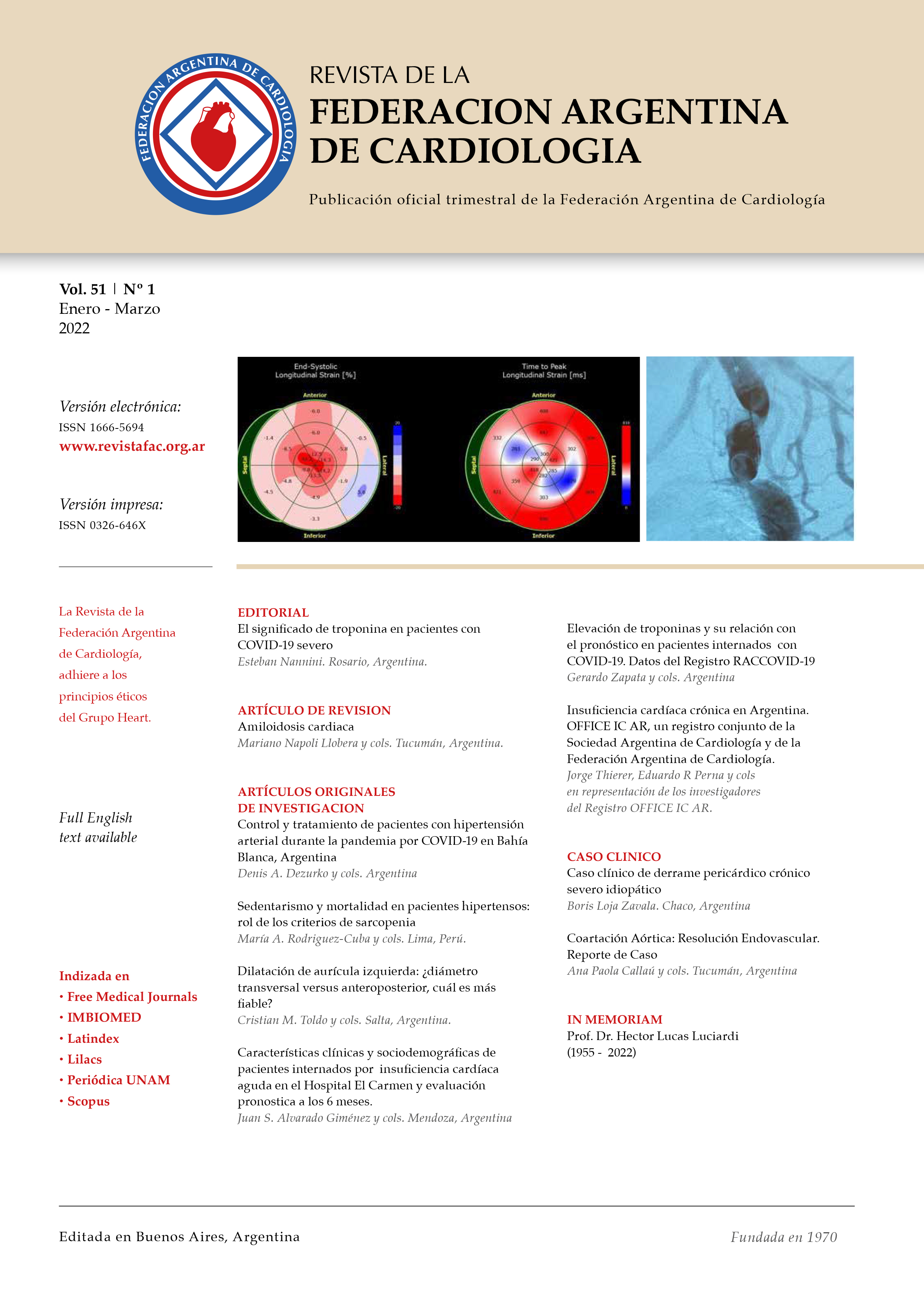
Cardiac Amyloidosis
Keywords:
Amyloidosis, Heart failure, Restrictive cardiomyopathyAbstract
Amyloidosis is a deposition disease, a consequence of the accumulation of amyloid protein fibers in the extracellular space of organs and soft tissue. There are more than 30 precursor proteins, with an unstable tertiary structure that fold, aggregate and deposit. Specifically, cardiac amyloidosis (CA) is a type of restrictive cardiomyopathy, in which the infiltration of amyloid fibers into myocardial tissue produces progressive ventricular stiffness, wall-thickening and diastolic dysfunction due to restrictive physiology, which typically manifests as heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. CA can clinically simulate other cardiovascular diseases, and recognizing “red flags” continues to be the main clinical challenge, being the first step towards a definitive diagnosis. The use of non-invasive techniques allows the early identification and treatment of this disease, the incidence and prevalence of which are still uncertain.